
What is Palatyne?
Palatyne is isomaltulose, a carbohydrate with a structure similar to table sugar. The difference lies in the 1,6 glycosidic bond that links them, causing the body to take four times longer to digest and absorb it than table sugar. This means blood sugar levels don’t spike rapidly after consumption [1]. Palatin is completely digested and absorbed in the small intestine and does not cause digestive side effects like stomach pain or diarrhea [2].
References
1. Sangeetha Shyam, Amutha Ramadas, Sui Kiat Chang, Isomaltulose: Recent evidence for health benefits, Journal of Functional Foods, Volume 48, 2018, Pages 173-178.
2. TAMURA, A., SHIOMI, T., TAMAKI, N., SHIGEMATSU, N., TOMITA, F., & HARA, H. (2004). Comparative Effect of Repeated Ingestion of Difructose Anhydride III and Palatinose on the Induction of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Humans. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 68(9), 1882–1887
A Carbohydrate with a Low Glycemic Index
Palatyne has a glycemic index (GI) of 38, classifying it as a low-GI food (less than 55). This means it has a significantly smaller impact on blood sugar levels compared to general sugars [1].
As shown in the graph, Palatyne’s low glycemic index means it does not cause an immediate spike in blood sugar after consumption and does not cause a significant drop in blood sugar levels 120 minutes after consumption. This demonstrates that Palatyne has a smaller effect on blood sugar levels compared to glucose.
References
1. Wantanee Kriangsinyos. (2010). A study of glycemic index, changes in blood glucose, and nutrient metabolism for energy utilization after ingestion of isomaltulose. Institute of Nutrition, Mahidol University.
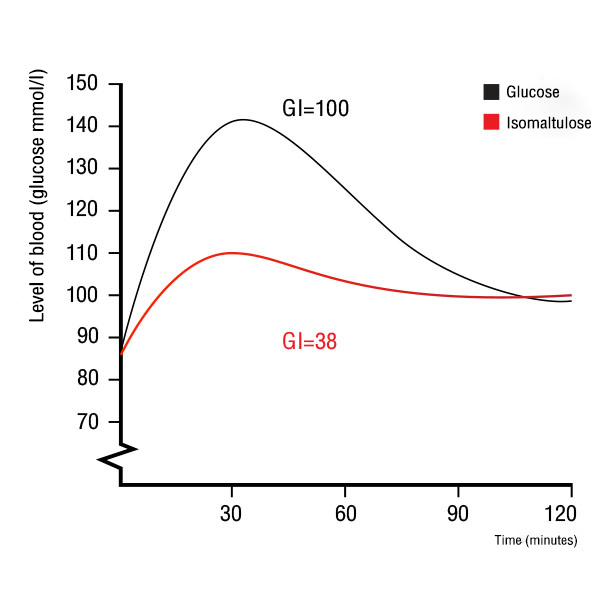
Graph Comparing the Effects of Palatyne and Glucose on Blood Sugar Levels

Isomaltulose and People with Diabetes
Research shows that isomaltulose is gentle for people with diabetes. A study on patients with type 2 diabetes found that consuming isomaltulose had a lesser effect on hormones that influence blood sugar levels and pancreatic function than consuming table sugar. This includes hormones like insulin, glucagon, and C-peptide. Therefore, Palatin has a positive effect on the body’s response to insulin (insulin sensitivity) and helps to slow the deterioration of the pancreas [1].
Additionally, isomaltulose can stimulate receptors in the small intestine, increasing the secretion of the incretin hormone GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide 1) by as much as 2 times when compared to consuming table sugar. GLP-1 is a crucial hormone for maintaining blood sugar balance in the body [1][2].
References
1.Maeda A, Miyagawa J, Miuchi M, et al. Effects of the naturally-occurring disaccharides, palatinose and sucrose, on incretin secretion in healthy non-obese subjects. J Diabetes Investig. 2013;4(3):281-286.
2.Ang M, Linn T. Comparison of the effects of slowly and rapidly absorbed carbohydrates on postprandial glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Oct;100(4):1059-68.
Sustained and Long-Lasting Energy
Palatyne is a carbohydrate that provides 4 kilocalories per 1 gram, the same as table sugar or other starches. The difference is in the structure of Palatin (isomaltulose), which is held together by an alpha-1,6 glycosidic bond. This means the body takes four times longer to digest and absorb it than table sugar [1]. As a result, glucose is released slowly into the bloodstream, providing the body with a continuous and prolonged energy supply.
Studies on athletes have shown that consuming drinks containing low-GI isomaltulose helps maintain stable blood glucose levels during exercise. This has a positive effect: it helps to delay fatigue, making it ideal for endurance exercises lasting more than 1 hour. It also allows the body to burn up to 20% more fat for energy compared to consuming high-GI drinks [2].
Blood glucose is also the primary energy source for the brain. If blood glucose levels drop significantly, the brain cannot function at its best. Therefore, isomaltulose’s ability to maintain stable blood glucose levels helps enhance brain performance and increase concentration.
In addition, studies in both children and adults have found that consuming foods containing isomaltulose leads to improved memory compared to consuming foods with regular sugar [3][4].

References
1.Sangeetha Shyam, Amutha Ramadas, Sui Kiat Chang, Isomaltulose: Recent evidence for health benefits, Journal of Functional Foods, Volume 48, 2018, Pages 173-178.
2.König D, Zdzieblik D, Holz A, Theis S, Gollhofer A. Substrate Utilization and Cycling Performance Following Palatinose™ Ingestion: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2016 Jun 23;8(7):390. doi: 10.3390/nu8070390. PMID: 27347996; PMCID: PMC4963866.
3.Hayley Young, David Benton, The glycemic load of meals, cognition and mood in middle and older aged adults with differences in glucose tolerance: A randomized trial, e-SPEN Journal, Volume 9, Issue 4, 2014, Pages e147-e154.
4.Young H, Benton D. The effect of using isomaltulose (Palatinose™) to modulate the glycaemic properties of breakfast on the cognitive performance of children. Eur J Nutr. 2015 Sep;54(6):1013-20. doi: 10.1007/s00394-014-0779-8. Epub 2014 Oct 14. PMID: 25311061; PMCID: PMC4540784.

Ideal for Weight Management
Over the past 20 years, many children and adults in Thailand have become overweight due to overeating and poor nutritional habits (Thai Health Promotion Foundation, 2021).
Today, most people trying to manage their weight believe they must severely restrict their food intake and avoid starches and sugars. However, the body still needs a complete range of nutrients to avoid deficiencies, especially an adequate amount of low-glycemic index carbohydrates, to maintain a healthy weight.
Palatyne Increases Fat Burning by Up to 20%
Palatyne is slowly digested and absorbed into the bloodstream as glucose, resulting in a lower insulin release. The insulin hormone promotes fat storage in the body. Studies have shown that Palatin (isomaltulose) helps reduce fat accumulation and increases fat oxidation by up to 20% more than regular table sugar [1]. It has also been found that long-term consumption of isomaltulose can significantly reduce triglyceride levels in the blood and decrease visceral fat [2][3], which is beneficial for those who want to manage their weight.
References
1. Sridonpai P, Komindr S, Kriengsinyos W. Impact of Isomaltulose and Sucrose Based Breakfasts on Postprandial Substrate Oxidation and Glycemic/Insulinemic Changes in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Subjects. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016 Mar;99(3):282-9. PMID: 27276739.
2. Brunner S, Holub I, Theis S, Gostner A, Melcher R, Wolf P, Amann-Gassner U, Scheppach W, Hauner H. Metabolic effects of replacing sucrose by isomaltulose in subjects with type 2 diabetes: a randomized double-blind trial. Diabetes Care. 2012 Jun;35(6):1249-51. doi: 10.2337/dc11-1485. Epub 2012 Apr 9.
3. Okuno M, Kim MK, Mizu M, Mori M, Mori H, Yamori Y. Palatinose-blended sugar compared with sucrose: different effects on insulin sensitivity after 12 weeks supplementation in sedentary adults. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2010 Sep;61(6):643-51.
Preserves Antioxidants in Food
Antioxidants are substances that can inhibit or slow down oxidation, which is the cause of free radicals in the body. Free radicals can damage cells, leading to the deterioration of organs and the breakdown of the immune system. Consuming foods with antioxidants helps to prevent chronic diseases and age-related illnesses. Examples of antioxidants found in food include Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, Carotenoids, and Polyphenols [1].
A study on Palatyne in green tea drinks found that Palatyne helps preserve polyphenols, which are antioxidants, in the food more effectively than table sugar. Furthermore, Palatyne enhances the ability of green tea to inhibit sugar absorption and reduce post-meal blood sugar levels more than using table sugar [2].

References
- “Antioxidants: In Depth”. NCCIH. June 2010. Archived from the originalon 25 August 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2018.
- Suraphad P, Suklaew PO, Ngamukote S, Adisakwattana S, Mäkynen K. The Effect of Isomaltulose Together with Green Tea on Glycemic Response and Antioxidant Capacity: A Single-Blind, Crossover Study in Healthy Subjects. Nutrients. 2017 May 6;9(5):464. doi: 10.3390/nu9050464. PMID: 28481230; PMCID: PMC5452194.

Promotes Relaxation
Modern society is changing rapidly, with changes in lifestyle, work, economics, politics, values, culture, and disease outbreaks. These factors can cause stress. If stress becomes excessive, it can impact both physical and mental health (Department of Mental Health, 2020). As a result, many products on the market today aim to help with stress relief.
Food is one factor that can help reduce stress, from the smell, taste, and appearance to ingredients that have a relaxing effect on the body. For example, Theanine, an amino acid found in green tea, affects neurotransmitters in the brain [1]. Even sugar, when consumed, provides energy to brain cells and stimulates the release of brain chemicals, making you feel refreshed and in a better mood. This is why drinking a sugary beverage can make you feel more energized and lively [2].
A study on the effect of brain waves on the body’s state found that the brain waves present during a calm, relaxed state are Alpha waves. This is the opposite of Beta waves, which occur during periods of thinking or stress. This study, conducted on 18 volunteers aged 21-40, examined the effect of isomaltulose on the generation of alpha brain waves. It found that consuming 40 grams of isomaltulose resulted in a significantly higher generation of alpha waves in the brain 150 minutes after consumption compared to sugar. Additionally, consuming isomaltulose with Theanine, which has stress-reducing effects, significantly increased the generation of alpha waves [3].
Palatyne (isomaltulose) helps the body relieve stress because it is slowly digested and absorbed into the bloodstream, preventing blood sugar levels from becoming too high or low. This ensures the brain receives a steady supply of energy and can efficiently produce brain waves and neurotransmitters. It also helps to enhance the effects of active ingredients in food that reduce stress.
References
1.Juneja, L.R., Chu, D.-C., Okubo, T., Nagato, Y. and Yokogoshi, H. (1999). L-Theanine: a unique amino acid of green tea and its relaxation effect in human. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 10. 199–204.
2. Martin, P.Y. and Benton, D. (1999). The influence of a glucose drink on a demanding working memory task. Physiol. Behav. 67. 69–74.
3. NAGAI, Yukie & SATO, Hiroshi & Kashimura, Jun & EBASHI, Tadashi & MACHI, Yoshio. (2003). Effect of Palatinose Administration on .ALPHA.1 Brain Waves in Human Volunteers. Food Science and Technology Research – FOOD SCI TECHNOL RES. 9. 357-360.


